The Federal Direct Parent PLUS loan plays a vital role in financing education by providing an option for parents of dependent undergraduate students to borrow funds to cover the cost of their children’s education. This credit-based loan allows parents to bridge the gap between college funds and educational expenses, ensuring that their children can pursue higher education without financial constraints.
With Parent PLUS loans, parents can borrow up to the total estimated cost of attendance minus other financial aid received. This loan provides a way to supplement other sources of college funding, giving families more flexibility in supporting their child’s education. The loan interest rate, determined annually by federal law, starts accruing once the funds are disbursed.
To be eligible for a Parent PLUS loan, parents must meet certain criteria. This includes being the biological or adoptive parent of the student, meeting citizenship requirements, and having a satisfactory credit history. The application process involves completing the online Federal Direct Parent PLUS Loan Application and signing a Master Promissory Note if approved.
Repayment of the loan begins 60 days after full disbursement, allowing parents time to adjust financially. Various repayment plans are available, offering flexibility in managing loan payments. Parent PLUS loans provide a valuable option for families to finance their children’s education, ensuring that educational opportunities remain accessible.
Key Takeaways
- Parent PLUS loans are credit-based loans that help parents finance their child’s education.
- These loans cover the cost of attendance minus other financial aid received.
- Eligibility requires being the biological or adoptive parent, meeting citizenship criteria, and having a satisfactory credit history.
- The application process involves completing the online application and signing a Master Promissory Note.
- Repayment of the loan starts 60 days after full disbursement, with various repayment plans available.
What is a Parent PLUS Loan?
The Parent PLUS loan, also known as the Direct PLUS Loan, is a federal loan offered to parents of dependent undergraduate students to help cover the cost of college or career school. It is a loan option for families who have exhausted federal student loans, grants, and scholarships. The loan does not have a cap on the borrowing amount and can be used to supplement other sources of financial aid.
Parents must meet eligibility criteria, including being a U.S. citizen or eligible non-citizen and having a dependent student enrolled at least half-time. The loan requires a credit check and the signing of a Master Promissory Note.
The Parent PLUS loan provides parents with the opportunity to financially support their child’s college education without a set limit on borrowing. This loan can fill the gap between available financial aid and the cost of attending college or career school.
Key Features of Parent PLUS Loans
- Available to parents of dependent undergraduate students
- No borrowing cap
- Can be used to supplement other financial aid
- Requires a credit check
- Must sign a Master Promissory Note
The Parent PLUS loan is a valuable resource for families seeking to finance their child’s college education. It allows parents to bridge the gap between available financial aid and the total cost of attending college or career school. However, it is important for parents to carefully consider the loan’s terms, interest rates, and repayment options before making a decision.
Eligibility and Application Process for Parent PLUS Loans
Parent PLUS loans provide parents with the opportunity to financially support their dependent undergraduate students’ education. However, to be eligible for a Parent PLUS loan, certain requirements must be met.
First and foremost, you must be the biological or adoptive parent of the student you are applying for. This loan program is specifically designed to assist parents in financing their children’s education. Additionally, you must be a U.S. citizen or eligible non-citizen to be considered eligible for a Parent PLUS loan.
Another important factor in determining eligibility is your credit history. A credit check will be performed as part of the application process to assess your creditworthiness. While some credit issues may not disqualify you outright, it’s crucial to have a satisfactory credit history to increase your chances of approval.
Moreover, your child must also meet the general eligibility requirements for financial aid. This includes being enrolled at least half-time in an eligible educational institution and maintaining satisfactory academic progress.
To apply for a Parent PLUS loan, you need to complete the Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA) and indicate your interest in the Parent PLUS loan option. The FAFSA is a standardized form that collects information about your financial situation, which helps determine your eligibility for various types of financial aid.
During the application process, it’s important to note that a credit check will be conducted. This check is intended to evaluate your creditworthiness and determine your eligibility for the loan. If approved, you will be required to sign a promissory note, which is a legal document stating your agreement to repay the borrowed funds.
It’s also worth mentioning that the loan amount you can receive through the Parent PLUS program is determined by the remaining cost of attendance after other financial aid, such as grants and scholarships, has been taken into account. This ensures that the loan serves as a supplemental resource rather than duplicating existing financial assistance.
Overall, applying for a Parent PLUS loan involves meeting specific eligibility criteria, completing the FAFSA, undergoing a credit check, and signing a promissory note if approved. It’s important to thoroughly understand the requirements and steps involved in the process to make informed decisions regarding your child’s educational funding.
| Eligibility Requirements |
|---|
| You must be the biological or adoptive parent of the student. |
| You must be a U.S. citizen or eligible non-citizen. |
| Your student must meet the general eligibility requirements for financial aid. |
| A credit check will be performed to assess your credit history. |
Interest Rates and Repayment of Parent PLUS Loans
Parent PLUS loans offer financing options for parents seeking to support their child’s higher education. Understanding the interest rates and repayment terms is crucial to effectively manage these loans.
The Role of Interest Rates
Parent PLUS loan interest rates are determined annually and remain fixed throughout the life of the loan. The specific interest rate varies depending on when the loan was disbursed. It’s essential to note that in addition to the interest rate, an origination fee may be deducted from the loan amount.
Loan Disbursement and Repayment
Repayment of the loan typically begins 60 days after the final disbursement. It is important to create a budget and plan for repayment to ensure timely payments. Parents have the option to request deferment, allowing for a delay in repayment while the student is enrolled at least half-time. This option provides flexibility when financial circumstances require it. Additionally, a six-month grace period is provided after the student leaves school, giving parents time to transition to loan repayment.
Repayment Plans
Various repayment plans are available to meet the needs of parents. Income-contingent plans consider the borrower’s income and family size when determining monthly payments. Extended repayment plans extend the repayment period beyond the standard 10-year term, resulting in lower monthly payments. Parents working in public service may qualify for loan forgiveness through the Public Service Loan Forgiveness program.
It is essential to evaluate the different repayment plans and choose the option that best suits your financial situation. Consider consulting with a financial advisor to determine the most suitable repayment plan for your needs.

Image showing an illustrative representation of Parent PLUS loan repayment
Parent PLUS Loans and Black Families
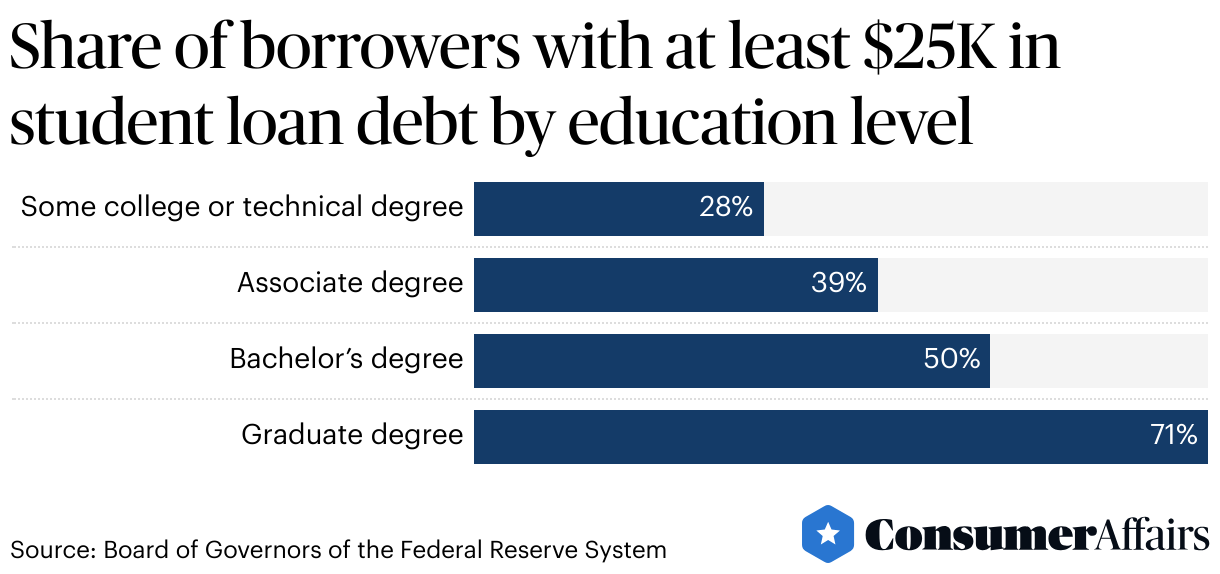
Black families have been found to take out Parent PLUS loans at a higher rate compared to other racial groups. These loans play a significant role in financing higher education for Black students.
Due to income disparities between Black and White families, Parent PLUS loans are often relied upon to cover the cost of college tuition. Black families see college education as a means of economic mobility and are willing to take on debt to provide their children with educational opportunities.
However, the repayment of these loans can be challenging for Black families, leading to prioritizing basic needs over loan repayments and impacting their financial health. As a result, student loan debt becomes a burden for many Black families.
To alleviate the reliance on Parent PLUS loans and improve higher education affordability, there is a need for comprehensive solutions. Increasing Pell Grants and implementing state-level investments in public higher education can help reduce the financial burden for Black families.
By addressing the challenges associated with student loan debt, we can create a more equitable system that ensures access to higher education for all students, regardless of their racial or economic backgrounds.
Impact on Higher Education Affordability
The higher rate at which Black families take out Parent PLUS loans highlights the affordability crisis in higher education. These families recognize the value of education and are determined to provide their children with the same opportunities as their peers.
However, the impact of student loan debt on Black families is significant. It not only affects their current financial situation but also has long-term implications for wealth accumulation and economic mobility.
Black borrowers often face higher interest rates, making loan repayment more challenging. The burden of student loan debt can hinder their ability to pursue other financial goals, such as homeownership or retirement savings.
In order to achieve true higher education affordability, it is essential to address the systemic issues that contribute to the reliance on Parent PLUS loans among Black families. This includes addressing income disparities, increasing access to scholarships and grants, and implementing policies that support college affordability for all students.
Credit Requirements and Loan Denial or Approval
In order to determine eligibility for Parent PLUS loans, a credit check is required. As a parent, you must meet certain credit requirements to be approved for the loan. One of the key factors is having a satisfactory credit history without any adverse marks. Adverse credit history may include late payments, defaults, bankruptcies, foreclosures, wage garnishments, or tax liens. It’s important to maintain a good credit standing to increase your chances of loan approval.
However, if you have an adverse credit history, it doesn’t necessarily mean that you will be denied a Parent PLUS loan. There are alternative options available to qualify for the loan. One option is to obtain a credit-worthy cosigner who can guarantee the repayment of the loan. Another option is to provide documentation of extenuating circumstances that contributed to the adverse credit history, which will be taken into consideration during the loan review process.
If your Parent PLUS loan application is denied, don’t worry. The student may still be eligible for additional federal student loans at a lower interest rate. Explore other loan options and financial aid resources to ensure that your child’s education is adequately funded.
Loan Denial – What Should You Do?
If your Parent PLUS loan application is denied, it’s important not to lose hope. Here are some steps you can take:
- Review your credit history: Take a close look at your credit report and identify any errors or discrepancies. If you find any, dispute them with the credit reporting agencies to correct your record.
- Consider a credit-worthy cosigner: If you have a family member or friend with good credit who is willing to cosign the loan, their positive credit history can strengthen your application.
- Explore other loan options: Research alternative loan programs and financial aid options that may be available to you and your child.
- Appeal the decision: If you believe your loan denial was unjustified, you can appeal the decision by providing additional documentation or explaining any extenuating circumstances that may have contributed to your adverse credit history.
Remember, each situation is unique, and it’s important to consult with a financial aid advisor or loan officer who can provide personalized guidance based on your circumstances.

| Common Reasons for Parent PLUS Loan Denial | Tips to Improve Approval Chances |
|---|---|
| An adverse credit history, such as late payments, defaults, bankruptcies, foreclosures, wage garnishments, or tax liens. | Improve your credit history by making all payments on time, reducing outstanding debts, and addressing any negative marks on your credit report. |
| A high debt-to-income ratio, indicating that you may struggle to meet loan repayments. | Pay down existing debts and reduce your monthly expenses to improve your debt-to-income ratio. |
| Insufficient income to support loan repayments. | Increase your income, explore employment opportunities, or consider a cosigner with a higher income to strengthen your loan application. |
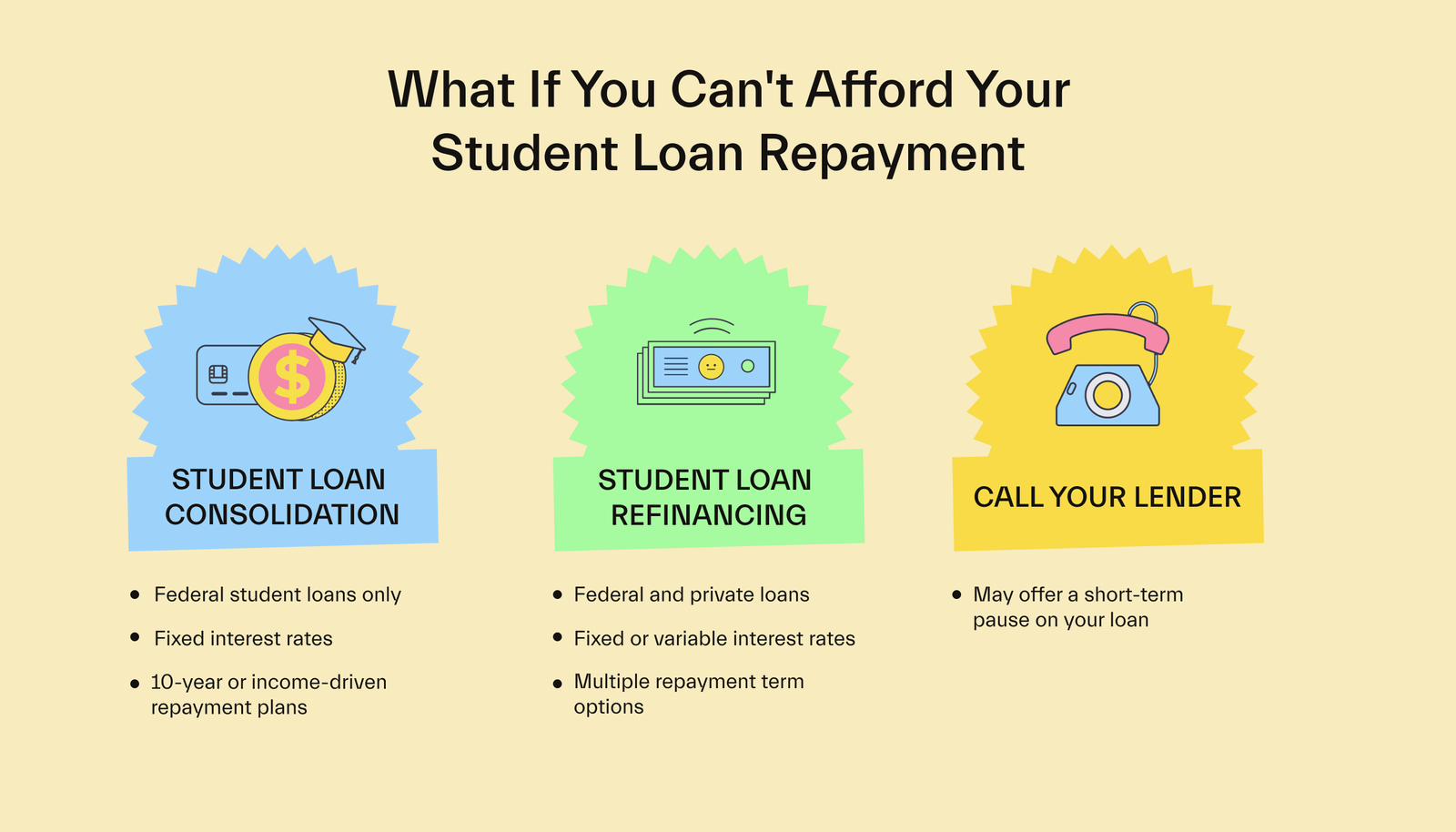
Repayment Options and Challenges for Parent PLUS Loans
Repaying Parent PLUS loans can present challenges for parents, particularly due to the higher interest rates compared to federal student loans. However, there are various repayment options available to provide flexibility and ease the financial burden.
One such option is the income-contingent repayment plan (ICR). This plan calculates your monthly payment based on your income and family size, making it more manageable and adjusted to your financial situation. With ICR, your payment amount may change each year as your income changes, ensuring that your loan payments align with your ability to pay.
Another repayment plan to consider is the extended repayment plan. This plan allows you to extend your repayment period beyond the standard 10 years, reducing your monthly payment amount. While this can provide temporary relief, keep in mind that extending the repayment period may result in higher overall interest payments.
Loan forgiveness programs are also available for Parent PLUS loans. The Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF) program offers loan forgiveness after 120 qualifying payments while working full-time for a qualifying employer, such as a government or non-profit organization. However, it is important to note that not all repayment plans are eligible for PSLF, so ensure you select an eligible plan if pursuing loan forgiveness.
Despite these options, repaying Parent PLUS loans can still pose challenges for many families. The higher interest rates can lead to larger overall loan amounts and more extended repayment periods. This can impact parents’ ability to meet their basic needs, save for retirement, or contribute to their children’s education-related expenses.
Additionally, unlike federal student loans, Parent PLUS loans do not offer the option to transfer repayment responsibility to the student. This means that parents are solely responsible for repaying the loan, even if their children are employed and financially capable of contributing.
Managing Parent PLUS loans requires careful consideration of your financial situation and long-term goals. It is crucial to understand the repayment options available, evaluate the impact on your financial health, and make informed decisions. Seeking financial guidance or working with a loan servicer can provide valuable insights and assistance in navigating the repayment process.
Parent PLUS loans play a crucial role in financing education and filling the gap in college funding for many families. These loans provide a solution for families who may not have sufficient resources to cover the full cost of college. However, it is important to acknowledge the challenges associated with Parent PLUS loans, such as higher interest rates and potential financial strain on parents.
Addressing income disparities and implementing various initiatives to increase college affordability can help reduce the reliance on Parent PLUS loans and ensure that education remains accessible for all students. By exploring alternative funding options and considering the long-term financial implications, families can make informed decisions about their college financing choices.
Parent PLUS loans should be viewed as one piece of the larger puzzle of education funding. It is important to evaluate each family’s unique financial situation and goals, and to consider other forms of financial aid, grants, scholarships, and work-study opportunities. By taking a comprehensive approach to college financing, families can make the most of the available resources and create a solid foundation for their children’s future.



1 thought on “The Role of Parent PLUS Loans in Financing Education”