Are you wondering if student loans are a good idea? In this article, we delve into the pros and cons of taking out student loans, helping you make an informed decision about financing your education.
Evaluating the Pros and Cons of Student Loans: Is Borrowing for Education Worth It?
Evaluating the Pros and Cons of Student Loans: Is Borrowing for Education Worth It?
When considering whether to borrow money for education, it is essential to weigh both the benefits and drawbacks of student loans. Here are some key points to consider:
Pros:
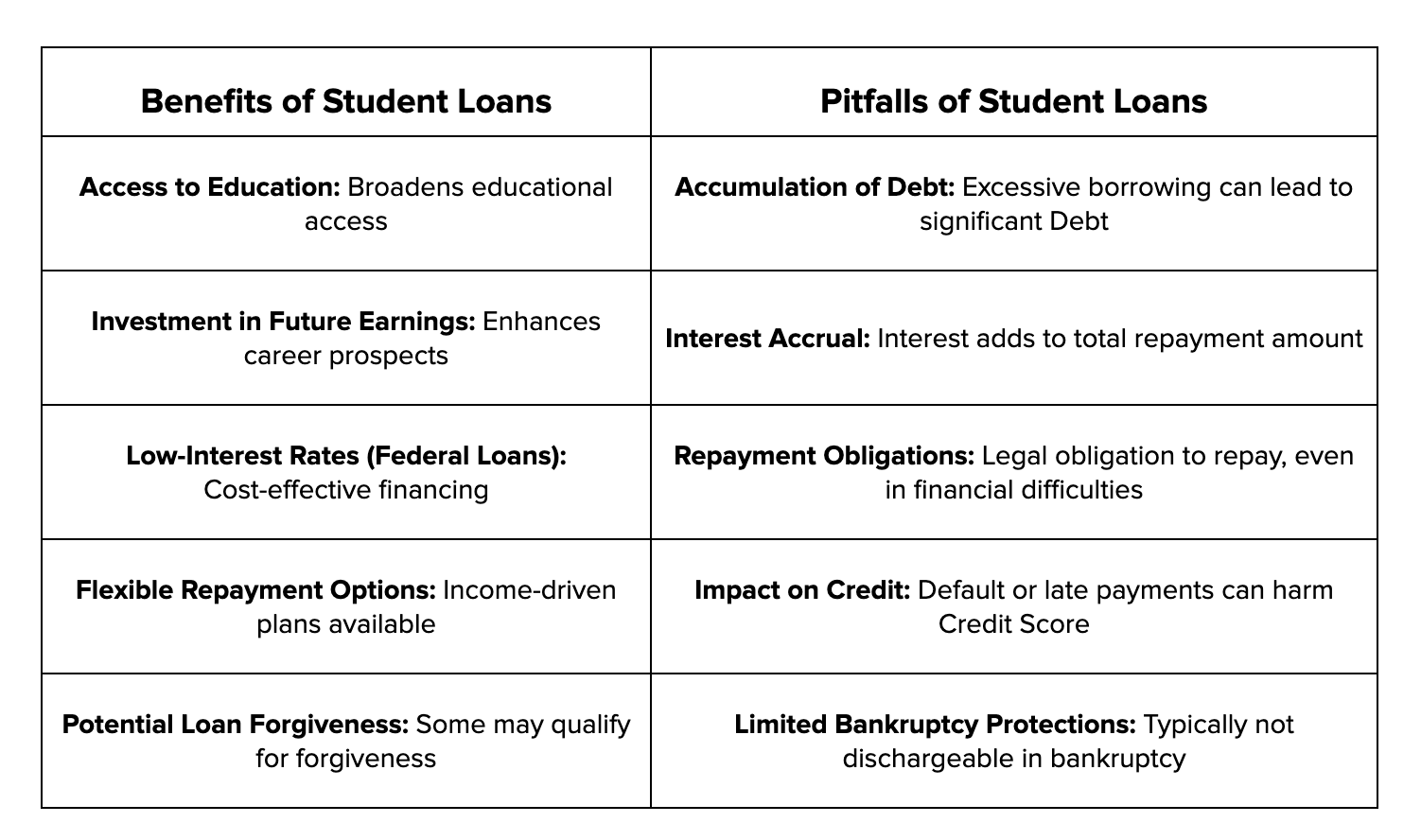
1. Access to Higher Education: Student loans make it possible for many students to pursue higher education who otherwise might not have the financial means. This allows access to a wide range of opportunities and career paths that require specialized training or degrees.
2. Investment in Future Earnings: Many studies indicate that individuals with college degrees tend to earn significantly more over their lifetimes compared to those with only a high school diploma. Therefore, taking out a loan can be seen as an investment in future earning potential.
3. Improved Career Opportunities: Higher education can open doors to jobs that offer better stability, benefits, and job satisfaction. Additionally, some fields require advanced degrees, necessitating student loans for entry into these professions.
4. Development of Financial Responsibility: Managing student loans can teach valuable lessons in financial responsibility, budgeting, and prioritization. These skills can be beneficial throughout life.
Cons:
1. Debt Burden: One of the most significant drawbacks is the sheer amount of debt students can accumulate. The burden of repaying this debt can be overwhelming and may take years or even decades to pay off.
2. Interest Accumulation: Interest on student loans can add up quickly, significantly increasing the total amount to be repaid over time. This can be especially challenging if interest starts accruing while still in school.
3. Impact on Credit Score: Failure to repay student loans promptly can negatively impact your credit score, affecting your ability to secure other forms of credit, such as mortgages or car loans, in the future.
4. Delayed Financial Milestones: High monthly loan payments can delay important life milestones, such as buying a house, starting a family, or saving for retirement. This can create long-term financial strain and dissatisfaction.
5. Mental Health Impact: The stress and anxiety associated with large amounts of debt can take a toll on mental health, potentially affecting overall well-being and quality of life.

Understanding the Different Types of Student Loans
Student loans come in various forms, primarily divided into federal and private loans. Federal student loans are offered by the government and typically provide more favorable terms and protections. These include Direct Subsidized Loans, Direct Unsubsidized Loans, and PLUS Loans. Direct Subsidized Loans are need-based, with the government covering interest while you’re in school or during deferment periods. Direct Unsubsidized Loans aren’t need-based, and you’re responsible for all interest accrued. PLUS Loans can cover the remaining costs not covered by other financial aid but require a credit check.
On the other hand, private student loans are provided by banks, credit unions, and other financial institutions. These loans tend to have higher interest rates and fewer borrower protections compared to federal loans. They might be necessary when federal aid doesn’t fully cover educational expenses, but they should be considered carefully due to the long-term financial commitment they entail.
The Long-Term Financial Impact of Student Loans
Taking on student loans can be an investment in your future, but it’s crucial to understand the long-term financial implications. Repayment terms can extend for decades, influencing decisions like buying a home, saving for retirement, or starting a family. Federal loans offer various repayment plans, including Income-Driven Repayment (IDR) plans that adjust your monthly payments based on income and family size, potentially providing affordable options for borrowers with lower incomes.
However, interest accrual over time can substantially increase the total amount repaid. For instance, if you extend the repayment period to lower monthly payments, you’ll end up paying more in interest overall. Additionally, if you miss payments or default, it can severely affect your credit score, making it harder to obtain other types of credit in the future.
Alternatives to Student Loans
Before committing to student loans, exploring alternatives can help reduce the amount you need to borrow. Scholarships and grants are an excellent first step since they don’t require repayment. Many organizations, schools, and governments offer scholarships based on merit, financial need, or specific talents. Applying for as many as possible can significantly offset education costs.
Additionally, consider work-study programs or part-time employment. Many colleges offer work-study opportunities that provide part-time jobs for students with financial need, allowing them to earn money to cover educational expenses. Alternatively, part-time jobs off-campus can also provide a steady income stream to manage costs.
Finally, attending a community college for the first two years before transferring to a four-year institution can drastically reduce tuition expenses, enabling you to save and potentially reduce borrowing needs. It’s important to weigh these alternatives and incorporate them into your financial planning to minimize debt and set a strong foundation for your financial future.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the long-term financial implications of taking out student loans?
Taking out student loans can have significant long-term financial implications. Interest accrual means you’re often paying back more than the original loan amount, which can impact your ability to save for retirement or make other major purchases like a home. Additionally, having substantial student debt can affect your credit score, influencing your eligibility for favorable interest rates on future loans. Proper understanding and planning are crucial to mitigating these long-term effects.
How do student loan interest rates compare to other forms of borrowing?
Student loan interest rates are generally lower than those for credit cards but can be higher than some secured loans like mortgages. Federal student loans typically offer fixed interest rates that are often more favorable compared to private loans, which may have either fixed or variable rates.
What are the potential risks and benefits of relying on student loans for education funding?
Relying on student loans for education funding has both benefits and risks.
Benefits:
- Access to Education: Student loans make higher education accessible when upfront funds are lacking.
- Credit Building: Successfully repaying student loans can help build a positive credit history.
Risks:
- Debt Burden: High loan amounts can lead to significant debt that may take years to repay.
- Interest Accumulation: Interest may accumulate, increasing the total amount to be repaid.
- Financial Stress: Large monthly payments can strain finances post-graduation, impacting lifestyle and savings.
In conclusion, the decision to take on student loans is a significant one that requires careful consideration of multiple factors. Student loans can provide access to higher education opportunities that might otherwise be financially unattainable. However, it is essential to weigh the potential long-term financial impact against the immediate benefits. Interest rates, repayment terms, and job prospects in your chosen field should all be part of this important decision-making process.
Furthermore, leveraging available resources and insights—such as those discussed in this article—can help you make an informed choice. Whether you decide to pursue higher education through student loans or seek alternative funding options, being well-informed is key to navigating the complexities of financing your education.
Finally, always remember to explore grants, scholarships, and other non-loan financial aids which can significantly reduce the burden of financing your education. By approaching this decision with a comprehensive understanding, you can better position yourself for both academic and financial success in the future.